Search
« Previous |
61 - 70 of 99
|
Next »
Search Results
Select an image to start the slideshow
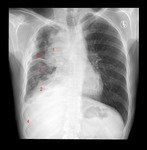
X-ray (chest), PA, Thymoma Invasive, Adult Male
1 of 10
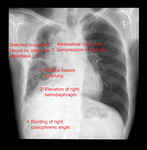
X-ray (chest), PA, Thymoma Invasive, Adult Male
2 of 10

X-ray (chest), PA, Thymoma, Adult Male
3 of 10
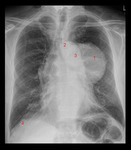
X-ray (chest), PA, Thymoma, Adult Male
4 of 10
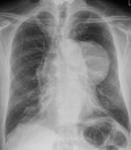
X-ray (chest), PA, Thymoma, Adult Male
5 of 10
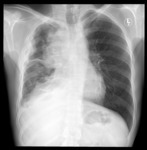
X-ray (chest), PA, Thymoma Invasive, Adult Male
6 of 10
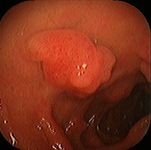
Duodenum, inflammed polyp of duodenal bulb
7 of 10
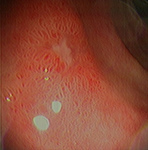
Duodenum, healing duodenal ulcer
8 of 10
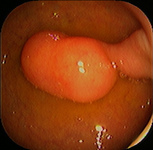
Duodenum, lipoma
9 of 10

Duodenum, hyperplastic polyp
10 of 10