Search
« Previous |
11 - 18 of 18
|
Next »
Search Results
Select an image to start the slideshow

Abdominal Pain 3. Epigastric Pain Differential Diagnosis and Approach
1 of 8

Abdominal Pain 10. Case Review
2 of 8
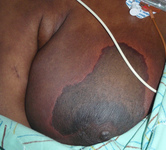
Dermatology: Warfarin-induced Skin Necrosis, Fatal, Breast
3 of 8
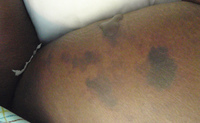
Dermatology: Skin, Warfarin-induced Skin Necrosis, Fatal
4 of 8
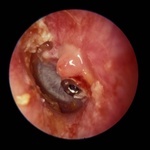
Tube Granuloma, Tympanic Membrane, Image 4
5 of 8
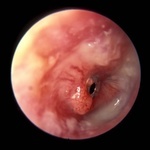
Tube Granuloma, Tympanic Membrane, Image 3
6 of 8
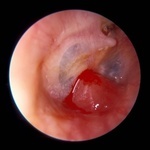
Tube Granuloma, Tympanic Membrane, Image 1
7 of 8
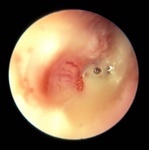
Tube Granuloma, Tympanic Membrane, Image 2
8 of 8