×
You need to sign in or sign up before continuing.
Search
« Previous |
41 - 50 of 507
|
Next »
Search Results
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Chronic Bullous Disease Of Childhood |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
Metropolitan Hospital Center, Kathryn Russel, MD |
| Rare autoimmune skin condition resulting in clusters of blisters developing in rings, often on the face or genitals. Also known as linear IgA disease. This case is shown on a child in Kenya. Note kwashiorkor body habitus and leukonychia in photo. |
| Keywords: |
Skin Diseases, Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis, Vancomycin, Immunoglobulin A, severe protein–energy malnutrition, Autoimmune Diseases, Kwashiorkor, Immunoglobulin G, Basement Membrane |
| Date Uploaded: |
02/03/2015 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Chronic Bullous Disease Of Childhood |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
Metropolitan Hospital Center, Kathryn Russel, MD |
| Rare autoimmune skin condition resulting in clusters of blisters developing in rings, often on the face or genitals. Also known as linear IgA disease. This case is shown on a child in Kenya. |
| Keywords: |
Basement Membrane, Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis, Skin Diseases, Autoimmune Diseases, Immunoglobulin A, severe protein–energy malnutrition, Immunoglobulin G, Vancomycin |
| Date Uploaded: |
02/02/2015 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Female External Genitalia |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
derivative work: Bobisbob (talk) - Jillvagina.jpg |
| Photograph showing external anatomy of female genitalia.
The female reproductive organs. The external organs include the vulva; Bartholin's glands; and clitoris. |
| Keywords: |
ob/gyn, Genitalia, Female, genitals, genitalia, obgyn, female sex organ, female genitals |
| Date Uploaded: |
01/15/2015 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Malignant Melanoma With Halo |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
National Cancer Institute |
| Central irregularly pigmented papule is surrounded by a 5mm rim of depigmentation due to a local immune response. Halo effect can also be seen surrounding benign nevi. |
| Keywords: |
Melanoma, melanoma, cancer, Neoplasms by Histologic Type, melanin, Nevi and Melanomas, Skin, Neoplasms, pigment, malignant, Neoplasms, Germ Cell and Embryonal |
| Date Uploaded: |
09/15/2014 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Malignant Melanoma |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
National Cancer Institute |
| Pigmented papule on the proximal arm with asymmetry, irregular border and red, brown, and black color variation. |
| Keywords: |
Nevi and Melanomas, malignant, Neoplasms, melanin, cancer, pigment, Skin, Neoplasms, Germ Cell and Embryonal, Neoplasms by Histologic Type, Melanoma, melanoma |
| Date Uploaded: |
09/15/2014 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Melanoma, Brown Lesion, Image 3 |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
Larry Meyer (Photographer) |
| A brown lesion with a large and irregular border on the skin.
Melanoma with characteristic asymmetry, border irregularity, color variation, and large diameter. |
| Keywords: |
Skin, malignant, Neoplasms, pigment, melanin, cancer, Neoplasms by Histologic Type, melanoma, Neoplasms, Germ Cell and Embryonal, Melanoma, Nevi and Melanomas |
| Date Uploaded: |
09/15/2014 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Melanoma In Situ |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
National Cancer Institute |
| Darkly pigmented central lesion surrounded by an ill-defined area of lighter tan pigmentation. Melanoma in situ represents a malignant melanocytic process that has not yet invaded into the dermis. |
| Keywords: |
malignant, pigment, cancer, Neoplasms, Germ Cell and Embryonal, Nevi and Melanomas, Skin, melanoma, Neoplasms by Histologic Type, Neoplasms, melanin, Melanoma |
| Date Uploaded: |
09/15/2014 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Melanoma |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
Larry Meyer (Photographer) |
| Melanoma |
| Keywords: |
malignant, Melanoma, Skin, Nevi and Melanomas, Neoplasms by Histologic Type, cancer, melanin, Neoplasms, Neoplasms, Germ Cell and Embryonal, melanoma, pigment |
| Date Uploaded: |
09/15/2014 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Macrograph: Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis (Images Only) |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
Mike Prystowsky, MD, PhD
Chairman, Department of Pathology
Yeshiva University, Albert Einstein School of Medicine |
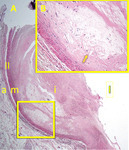
| Figure 1. Coronary artery with early atheroma and fibrous cap formation.
A. Gross macrophotograph of a longitudinally sectioned coronary artery. L indicates the lumen. The box marks a region with an early atheromatous lesion, as shown in the photomicrograph below it (B). The thin arrow to the right of the box marks a region with a more advanced lesion (see figure 2).
B. Microphotograph of the early atheromatous lesion as seen in the boxed area in A. This image shows the full thickness of the coronary artery wall, from adventitia at the bottom to lumen at the top. Layers of the artery are indicated by lowercase letters on the right side of the image: l = lumen, I = intima, m = media, a = adventitia. The two yellow lines on both sides of the image mark the boundary between the predominantly smooth-muscle arterial media at the bottom, and the thickened fibrotic intima at the top of the image. The more clear, pale-pink areas within the intima contain lipid, both intra- and extracellular. H&E stain, original magnification 4X.
Figure 2. Coronary artery with a more advanced atheroma showing coalesced intimal lipid under a still thick fibrous cap.
A. Microphotograph, low magnification full thickness view of a coronary artery wall cross section. Lowercase letters indicate the layers of the artery: a = adventitia, m = media, I = intima, l = lumen. Two short vertical lines delineate the markedly thinned arterial media. H&E stain, original magnification 4X.
B. High magnification view of the lipid pool inside the boxed area in A. Note the needle-shaped crystals of cholesterol, most visible at the edge of the lipid pool, as indicated by the arrow.
Figure 3. Coronary artery with an advanced atheroma.
A. Macrophotograph of a cross section of a coronary artery showing near-total lumenal occlusion by a raised atheroma (inside box).
B. Microphotograph of a cross section of the coronary artery, showing multiple raised atheromatous plaques, as indicated by Ps. Although there is still some lipid present, it has been mostly replaced by fibrosis and calcification, the latter marked by Ca in the image and indicated by blue areas or white voids where it was lost during histologic preparation. |
| Keywords: |
Vascular Diseases, Atherosclerosis, plaques, Heart disease, thickening |
| Date Uploaded: |
07/09/2014 |
-
| show more |
| Title: |
Macrograph: Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis (Images Only) |
| Depositor: |
batchuser@i-human.com |
| Creator: |
Mike Prystowsky, MD, PhD
Chairman, Department of Pathology
Yeshiva University, Albert Einstein School of Medicine |
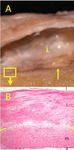
| Figure 1. Coronary artery with early atheroma and fibrous cap formation.
A. Gross macrophotograph of a longitudinally sectioned coronary artery. L indicates the lumen. The box marks a region with an early atheromatous lesion, as shown in the photomicrograph below it (B). The thin arrow to the right of the box marks a region with a more advanced lesion (see figure 2).
B. Microphotograph of the early atheromatous lesion as seen in the boxed area in A. This image shows the full thickness of the coronary artery wall, from adventitia at the bottom to lumen at the top. Layers of the artery are indicated by lowercase letters on the right side of the image: l = lumen, I = intima, m = media, a = adventitia. The two yellow lines on both sides of the image mark the boundary between the predominantly smooth-muscle arterial media at the bottom, and the thickened fibrotic intima at the top of the image. The more clear, pale-pink areas within the intima contain lipid, both intra- and extracellular. H&E stain, original magnification 4X.
Figure 2. Coronary artery with a more advanced atheroma showing coalesced intimal lipid under a still thick fibrous cap.
A. Microphotograph, low magnification full thickness view of a coronary artery wall cross section. Lowercase letters indicate the layers of the artery: a = adventitia, m = media, I = intima, l = lumen. Two short vertical lines delineate the markedly thinned arterial media. H&E stain, original magnification 4X.
B. High magnification view of the lipid pool inside the boxed area in A. Note the needle-shaped crystals of cholesterol, most visible at the edge of the lipid pool, as indicated by the arrow.
Figure 3. Coronary artery with an advanced atheroma.
A. Macrophotograph of a cross section of a coronary artery showing near-total lumenal occlusion by a raised atheroma (inside box).
B. Microphotograph of a cross section of the coronary artery, showing multiple raised atheromatous plaques, as indicated by Ps. Although there is still some lipid present, it has been mostly replaced by fibrosis and calcification, the latter marked by Ca in the image and indicated by blue areas or white voids where it was lost during histologic preparation. |
| Keywords: |
thickening, Vascular Diseases, plaques, Atherosclerosis, Heart disease |
| Date Uploaded: |
07/09/2014 |